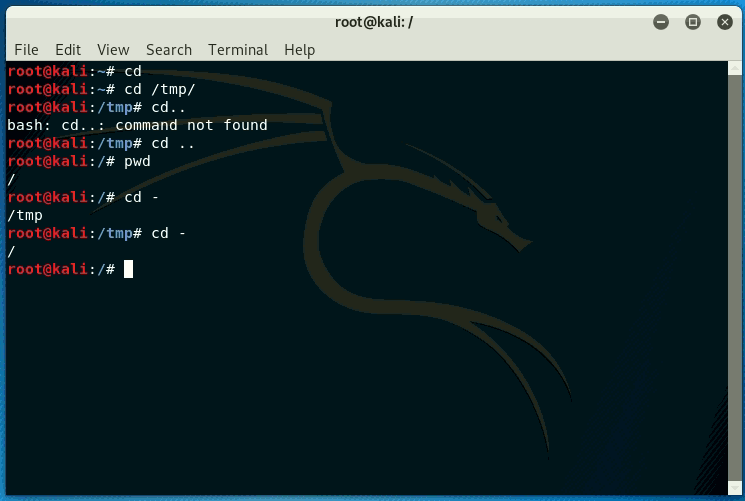
Let's see some important and commonly used commands in Kali Linux:
| Commands | Description |
|---|---|
| # history | This command is used to print the bash history of the current user. |
| # free | It gives the information about the available RAM and the total used and available spaces of physical memory and swap memory with buffer used by Kernal. |
| # vi | It is a screen editor used to edit the file. |
| # sort | It sorts the content of a text file line by line. |
| # more | It is used to display output in the terminal, one page at a time. |
| # less | It is used to view the file instead of opening the file. |
| # date | This command is used to display the system date and time. |
| # cal | It will display a formatted calendar of the current month. |
| # whoami | It will print the active user ID. |
| # pwd | It stands for "Print Working Directory" which prints the name of the working directory. |
| # ls | It is used to list out all the hidden files of a directory with -an attribute. |
| # users | It will display login names of the user currently logged in to the system. |
| # uptime | It will return you the time for which the system has been up. |
| # uname | It prints information about the current system. |
| # rm | It is used to delete files and directories. |
| # mv | This command moves, or renames, files, and directories on your file system. |
| # cp | It is used to copy files. |
| # cat | It is used to create single or multiple files, view contained file, concatenate files, and redirect output in terminal or files. |
| # mkdir | It is used to create directories. |
| # cd | It is used to change or switch the current working directory. |
Command structure:
- Changes the tools behaviour
- Letter preceded by a hyphen
- Can be grouped
- E.g. ls -alt
- Word preceded by double hyphen
- E.g. ls -help
Command arguments
It is an extra piece of information to tell the command what to act on. If we are using an option, argument comes after it. For example - ls -l /Desktop
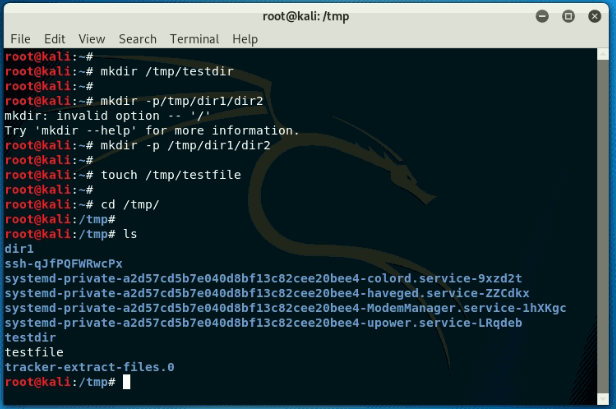
Creating Directories in Kali Linux
- To create directories, type-in mkdir /tmp/testdir inside the terminal. It will create a directory with name tetsdir.
- To create parent dir, type-in mkdir -p /tmp/dir1/dir2.
- To create a file inside a directory type-in touch /tmp/testfile.
- To view the directory use the ls command.
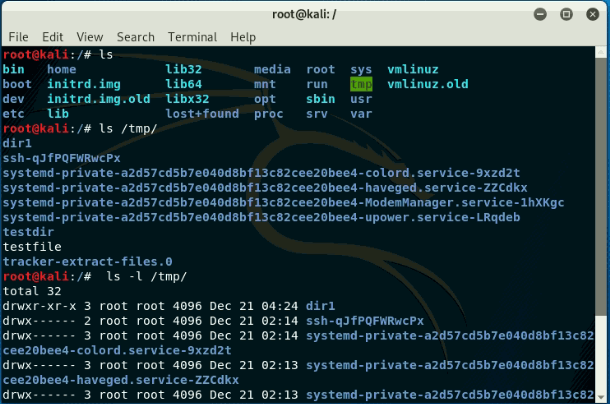
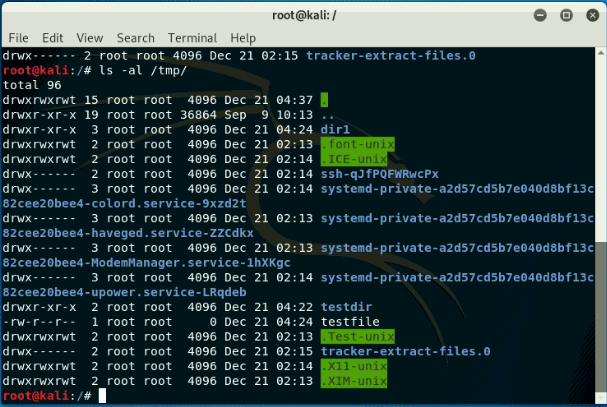
Listing Directory Content
- -l -long listing
- -a -list hidden files
- -r -list in reverse name
- -t -list new files first
- -rt -list in reverse time (older first)
Tags
How To