Configuring Kali Linux
Once we boot Kali Linux, we will have Kali's main menu that is organized by theme with the various types of tasks and activities that are relevant for the penetration tester and other security professionals as 0073hown in Figure below.
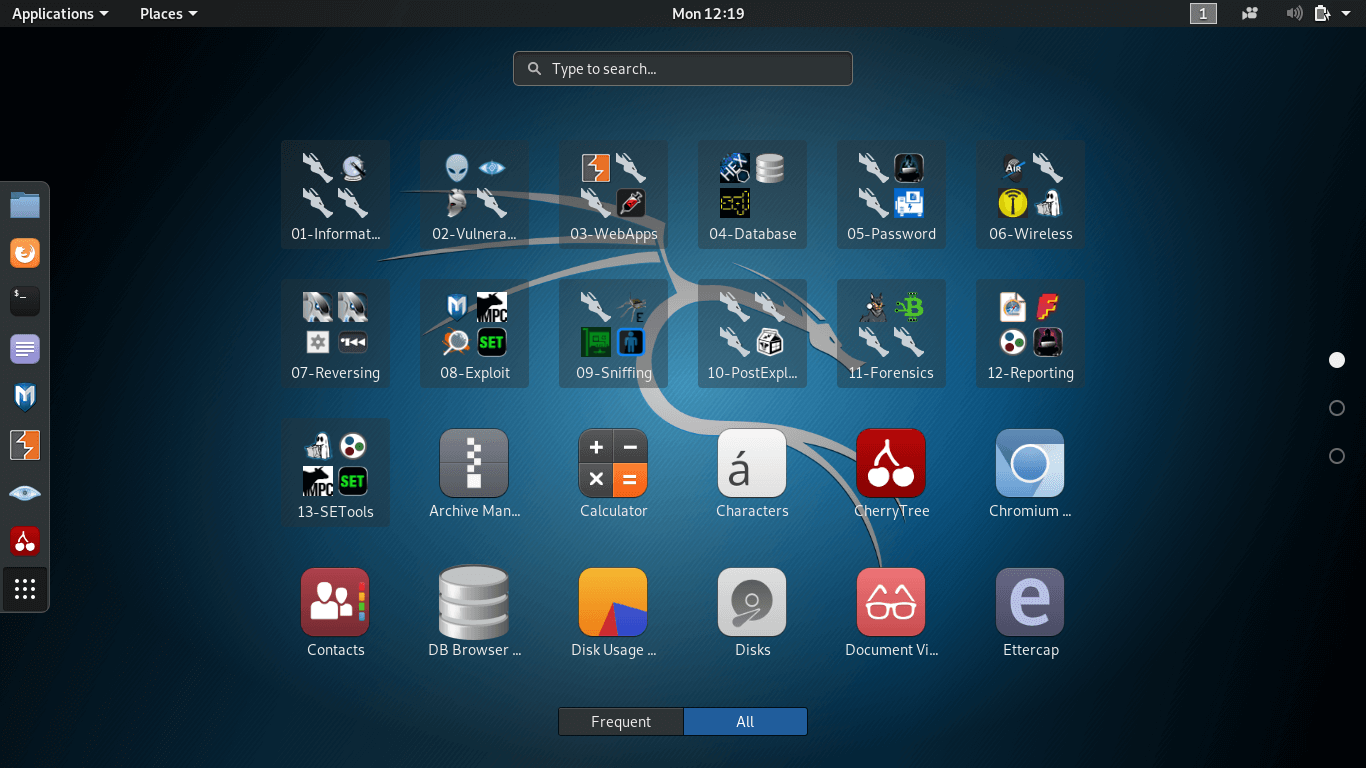
The task and activities are:
- Information Gathering: The process of collecting data about the target network/computer to identify potentially sensitive parts of the information system.
- Vulnerability Analysis: It will quickly test whether a local or remote system is affected by potential vulnerabilities and insecure configuration.
- Web application Analysis: It identifies misconfiguration and security weakness in web applications.
- Database Assessment: It contains the tools that test for attack vectors ranging from SQL injection to data extraction and analysis.
- Password Attacks: It contains online password attack tools and offline attack tools against the encryption or hashing systems.
- Wireless Attacks: It contains the tools that provide a wide range of support for multiple wireless cards.
- Reverse Engineering: It is used to analyze malware employed in targeted attacks.
- Exploitation Tools: It provides tools that allow us to write exploits and gain control over remote devices to take advantage of a vulnerability.
- Sniffing & Spoofing: Spoofing tools allows us to mimic an authorized user and Sniffing tools that helps us to capture and analyze data. Together these tools can be powerful.
- Post Exploitation: Tools that assist in maintaining the access of a system or need to extend control by laterally moving across the network.
- Forensics: It is a live boot environment that contains the tools that help us in full analysis and case management.
- Reporting Tools: It includes the tools that bring the data together, which is collected from various information-gathering tools and discover unreliable relationships.
- Social Engineer Tools: Tools that work as a medic during attacks. Such as, a USB key that is plugged in, which contains a harmful pdf, or it was also a Trojan horse that installed a backdoor. Or any banking website, in which the accountant is logged-in contains a perfect copy used for phishing purposes.
- System Service: It includes the tools that allow you to start and stop applications that run in the background as system services.
Kali Linux configuration
How to configure Network in Kali Linux
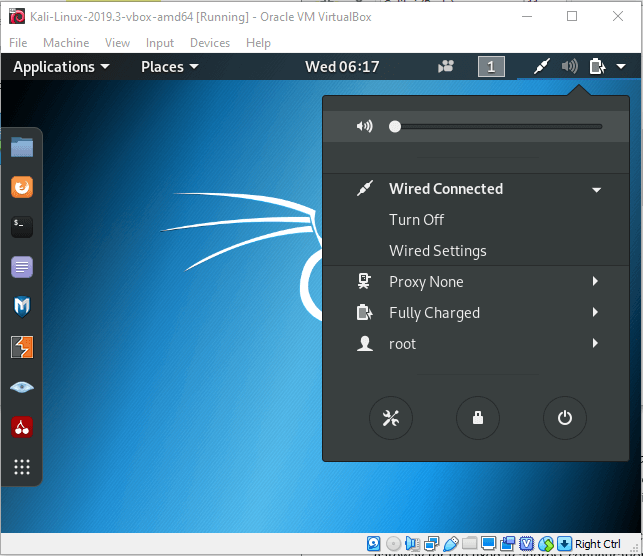
1. On the Desktop with NetworkManager: In Kali Linux, the NetworkManager is already installed and can be configured through GNOME's control center or through the top-right menu on Desktop as shown in Figure below.
2. On the Command-line with "ifupdown" command: When we want to configure the network settings without using the graphical desktop, we can use the command-line with the already-installed package i.e., ifupdown. It has Ifup and Ifdown tool. The network device can be removed at any time with the ifdown network device. And can modify and back up the network using the ifup network device.
And for wireless interfaces, we need the wpasupplicant package, which is included in Kali by default. The most commonly used options are WPA-SSID (defines the name of the wireless network to join) and WPA-PSK (defines the key protecting the network).
Note: You must provide more details such as IP address, the network, and the IP of the gateway for the fixed IP address configuration.
3. On the Command-line with "systemd-networkd" command: The ifupdown approach is a legacy tool used by Debian but still used as the default for server and other minimal installations. The new tool is introduced in the Kali for Network Configuration, which is systemd-networkd. It's integration with the init system makes it an attractive choice. You can configure these by placing the network files into the /etc/systemd/network/directory.
How to update Kali Linux
Step 1: We need to configure Kali Linux Repositories. /etc/apt/sources.list file must contain the following official Kali repositories:
Step 2: Updating Kali Linux by first updating the package list. Open terminal and enter:
Step 3: After updating the package list, update kept back packages
Step 4: Uninstall those packages that are no longer required.